Reset Windows Password:
remove user personal information
Selecting data source
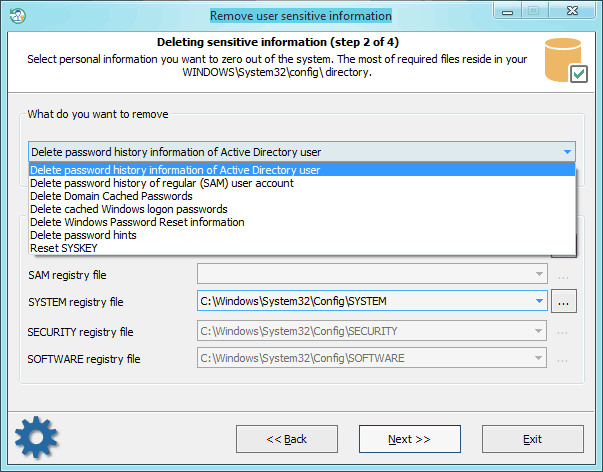
The program has a number of advanced features. One of them is deleting information that can be used by potential malefactors for recovering account passwords on your computer. Be careful; the information will be removed permanently with no chances for recovery. So, it includes the following items:
- Deleting password history for standard (SAM) and Active Directory user accounts. SAM password history, for example, is set in the group policy of the local computer. Hit Win+R keys, then type gpedit.msc, and click OK. Under Computer Configuration, drill down under Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options. Here look for policy: Interactive Logon: Number of previous logons to cache.
- Deleting domain cached passwords. More on cached domain passwords can be read here.
- Deleting cached Windows logon password.
- Deleting password reset diskette information. With that information and the password reset disk, one can easily recover the original textual password.
- Deleting password hints.
- Resetting SYSKEY security.
To continue with the program, provide (or select from available) the following files:
Deletion of AD password history - SYSTEM registry file and Active Directory database file (ntds.dit);
Deletion of SAM password history - SAM and SYSTEM registry files;
Deletion of cached domain passwords - files SECURITY and SYSTEM;
Deletion of cached logon passwords - files SECURITY, SOFTWARE, and SYSTEM;
Deletion of password reset disk information - files SAM, SECURITY, and SYSTEM;
Deletion of password hints - SAM, SOFTWARE, and SYSTEM
SYSKEY resetting - SAM, SECURITY, and SYSTEM
All registry files, except Active Directory database, are stored in the following directory %WINDIR%\system32\config. Where %WINDIR% stands for the Windows folder, by default - C:\Windows.
The location of the AD database is set during installation. By default, that's the %WINDIR%\NTDS folder.