Reset Windows Password:
password policy editor
Sometimes to functioning security settings properly, it is vitally required to set up the policy of the target workstation or a domain. For example, if you want to deny domain users to log on to a system without supplying strong passwords, you should restrict it through the domain password policy. However, that would be quite a problem if you cannot log on to the workstation or to the domain as an administrator. The new RWP's password policy editor can get around the problem and allows changing various password policy properties on any Windows system offline, without logging on to the system.
Selecting data source
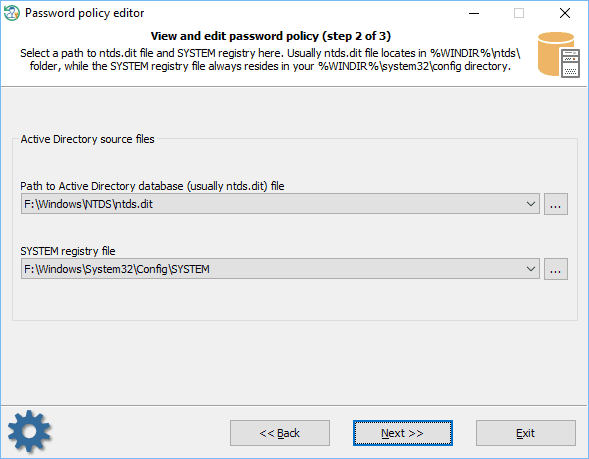
First of all, you will need to feed the program with two system files:
- either SAM and SYSTEM, in case you want to modify the password policy of a workstation or a standalone PC;
- or NTDS.DIT and SYSTEM, when you need to change the password policy properties of a domain.
The program should try to find the files automatically. You can, however, provide the paths manually.
Password policy editor
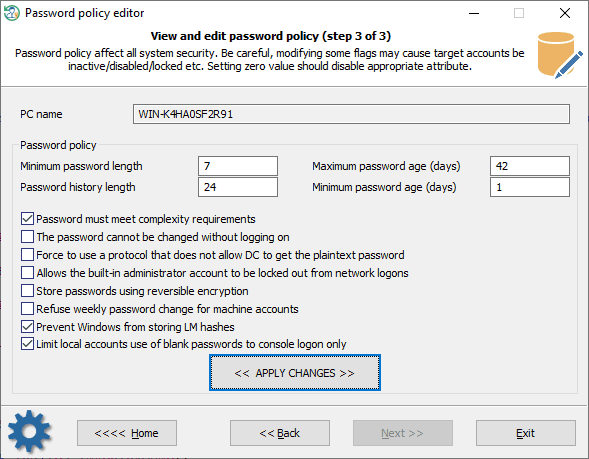
Here's a short description of what you can modify in the password policy of the target system:
- Minimum password length - minimum length of a valid password, in characters.
- Password history length - the number of previous passwords saved in the history list. A user is not allowed to reuse a password from the list.
- Maximum password age - maximum length (in days) that a password can remain the same. Passwords older than this must be changed.
- Minimum password age - minimum length of time before a password can be changed.
- Password must meet complexity requirements - passwords must meet the following minimum requirements: contain no user's account name or a part of it, be at least six characters in length (if otherwise is not set), contain characters from at least three charsets, do not be one used previously (if password history is set).
- The password cannot be changed without logging on - the password cannot be changed without logging on. Otherwise, if it has expired, you can change it and then log on.
- Force to use a protocol that does not allow DC to get the plaintext password - forces the client to use a protocol that does not allow the domain controller to get plaintext passwords.
- Allows the built-in administrator account to be locked out from network logons.
- Store passwords using reversible encryption - force to store plaintext passwords for all users instead of hashing the passwords.
- Refuse weekly password change for machine accounts - removes the requirement for any machine account to automatically change its password every week.
- Prevent Windows from storing LM hashes. The LAN Manager hash uses an extremely weak encryption algorithm. This setting controls whether a LM hash of the password can be stored in Active Directory and the local SAM database (the next time a new user is created or the password is changed). This setting is on by default on Windows Vista and later OSes.
- Limit local accounts to use blank passwords to console logon only. Prevent accounts with blank passwords from existing on a system. However, if a local account with a blank password did exist, enabling this setting will prevent network access, limiting the account to local console logon only.
To disable an editable attribute, just set zero value into its edit box.
Be careful, altering any value of the password policy will affect all security of the Windows system!