31.07.2024
Passcape ISO Burner v2.3.2
Some minor improvements
17.04.2024
Reset Windows Password v14.2
Telegram data recovery, Photo Database and Media Player investigation tools, and some more
Reset Windows Password v14.2
Telegram data recovery, Photo Database and Media Player investigation tools, and some more
Reset Windows Password:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Description |
| Allow users to select when a password is required when resuming from connected standby | This setting allows you to control whether a user can change the time before a password is required when a Connected Standby device screen turns off. If you enable this setting, a user on a Connected Standby device can change the amount of time after the device's screen turns off before a password is required when waking the device. If you disable this setting, a user cannot change the amount of time after the device's screen turns off before a password is required when waking the device. Instead, a password is required immediately after the screen turns off. |
| Default domain for logon | Specifies a default logon domain, which might be a different domain than the domain to which the computer is joined. |
| Do not enumerate connected users on domain-joined computers | If you enable this setting, the Logon UI will not enumerate any connected users on domain-joined computers. |
| Enumerate local users on domain-joined computers | If you enable this setting, Logon UI will enumerate all local users on domain-joined computers. |
| Turn off picture password sign-in for domain users | This setting allows you to control whether a domain user can sign in using a picture password. |
| Turn on convenience PIN sign-in for domain users | If you enable this setting, a domain user can set up and sign in with a convenience PIN. Note: The user's domain password will be cached in the system vault when using this feature. |
| Report when logon server was not available during user logon | This setting controls whether the logged-on user should be notified if the logon server could not be contacted during logon and he has been logged on using previously stored account information. |
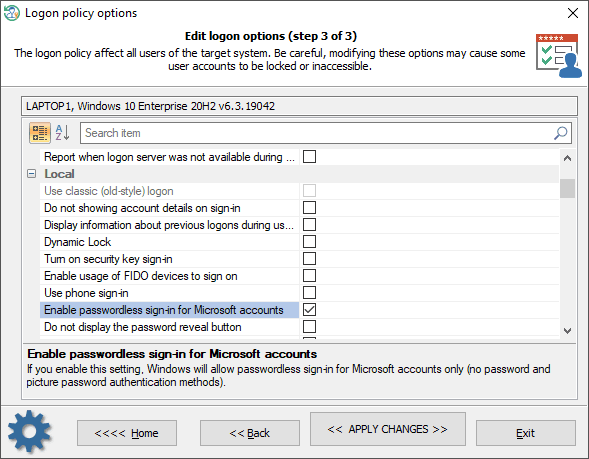
The setting of the Local group:
| Name | Description |
| Use classic (old-style) logon | Always use classic logon interface scheme. |
| Do not show account details on sign-in | If set, prevents the user from showing account details (email address or user name) on the sign-in screen. |
| Display information about previous logons during user logon | If you enable this setting, a message appears after the user logs on that displays the date and time of the last successful logon by that user, the date and time of the last unsuccessful logon attempted with that user name, and the number of unsuccessful logons since the last successful logon by that user. |
| Dynamic Lock | If you enable this setting, Windows will enable dynamic lock for all users on managed devices and users will not be allowed to disable the dynamic lock on their accounts. |
| Turn on security key sign-in | If you enable this setting, users can sign in with external security keys. |
| Enable usage of FIDO devices to sign on | This setting allows users to use a FIDO device, such as a phone, NFC card, to sign on to a desktop computer running Windows 10. |
| Use phone sign-in | If you enable this setting, phone sign-in will be enabled, allowing the use of a phone as a companion device for desktop authentication. |
| Enable passwordless sign-in for Microsoft accounts | If you enable this setting, Windows will allow passwordless sign-in (for Microsoft accounts only): both password and picture password authentication methods will be turned off. |
| Do not display the password reveal button | If you enable this setting, the password reveal button will not be displayed after a user types a password in the password entry text box. |
| Prevent the use of security questions for local accounts | If you turn this setting on, local users won't be able to set up and use security questions to reset their passwords. |
| Allow companion device for secondary authentication | If you enable or do not configure this setting, users can authenticate to Windows Hello using a companion device. Such as a phone, fitness band, or IoT device. |
| Software Secure Attention Sequence | This setting controls whether or not the software can simulate the Secure Attention Sequence (SAS). |
| The mode of automatically signing in and locking last interactive user after a restart or cold boot | This setting controls the configuration under which an automatic restart and sign on and lock occurs after a restart or cold boot. |
| Sign-in and lock last interactive user automatically after a restart | This setting controls whether a device will automatically sign in and lock the last interactive user after the system restarts or after a shutdown and cold boot. This only occurs if the last interactive user didn't sign out before the restart or shutdown. |
The setting of the Misc group:
| Name | Description |
| Always use custom logon background | If you enable this policy setting, the logon screen always attempts to load a custom background instead of the Windows-branded logon background. |
| Show clear logon background | This setting disables the acrylic blur effect on logon background image. |
| Do not display the Getting Started welcome screen at logon | If you enable this setting, the welcome screen is hidden from the user logging on to the system. |
| Turn off app notifications on the lock screen | This setting allows you to prevent app notifications from appearing on the lock screen. |
| Show first sign-in animation | This setting allows you to control whether users see the first sign-in animation when signing in to the computer for the first time. |
| Turn off Windows Startup sound | Turn off Windows sounds during authentication. |
| Do not process the legacy run list | This setting ignores the customized run list (programs and services that the system starts). |
| Do not process the run once list | If you enable this setting, the system ignores the list of additional programs and documents that are started automatically the next time the system starts. The customized run-once lists are stored in the registry in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\runOnce. |
| Hide entry points for Fast User Switching | This setting allows you to hide the Switch User interface in the Logon UI, the Start menu, and the Task Manager. |
| Block all consumer Microsoft account user authentication | If this setting is enabled, all applications and services on the device are prevented from using Microsoft accounts for authentication. |
| Default credential provider | Assign a specified credential provider as the default credential provider. |
| Exclude credential providers | This setting allows the administrator to exclude the specified credential providers from use during authentication. |
The setting of the Network group:
| Name | Description |
| Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon | Determines whether computers wait for the network to be fully initialized during startup and user logon. By default, computers do not wait for the network to be fully initialized at startup and logon. |
| Do not display network selection UI | If you enable this setting, the PC's network connectivity state cannot be changed without signing into Windows. |
The setting of the Biometrics group:
| Name | Description |
| Allow domain users to log on using biometrics | If you enable or do not configure this setting, Windows allows domain users to log on to a domain-joined computer using biometrics. |
| Allow users to log on using biometrics | If you enable or do not configure this setting, all users can log on to a local Windows-based computer and can elevate permissions with UAC using biometrics. |
| Allow the use of biometrics | If you enable or do not configure this setting, the Windows Biometric Service is available, and users can run applications that use biometrics on Windows. |
| Configure enhanced anti-spoofing | If you enable this setting, Windows requires all users on managed devices to use enhanced anti-spoofing for Windows Hello face authentication. This disables Windows Hello face authentication on devices that do not support enhanced anti-spoofing. |
| Specify a timeout for fast user switching events | This setting specifies the number of seconds a pending fast user switch event will remain active before the switch is initiated. By default, a fast user switch event is active for 10 seconds before becoming inactive. |
The setting of the PIN group:
| Name | Description |
| PIN expiration | This setting specifies the period of time in days (between 1 and 730) that a PIN can be used before the system requires the user to change it. |
| PIN history | This setting specifies the number of past PINs that can be associated with a user account that can't be reused. The value must be between 0 to 50 PINs. |
| Maximum PIN length | Maximum PIN length configures the maximum number of characters allowed for the PIN. The largest number you can configure for this policy setting is 127. |
| Minimum PIN length | Minimum PIN length configures the minimum number of characters required for the PIN. The lowest number you can configure for this policy setting is 4. |
| Require digits | If you enable or do not configure this setting, Windows requires users to include at least one digit in their PIN. |
| Require lowercase letters | If you enable this setting, Windows requires users to include at least one lowercase letter in their PIN. |
| Require special characters | If you enable this policy setting, Windows requires users to include at least one special character in their PIN. |
| Require uppercase letters | If you enable this policy setting, Windows requires users to include at least one uppercase letter in their PIN. |
The setting of the Windows Hello group:
| Name | Description |
| Allow enumeration of emulated smart card for all users | Windows prevents users on the same computer from enumerating provisioned Windows Hello for Business credentials for other users. If you enable this setting, Windows allows all users of the computer to enumerate all Windows Hello for Business credentials, but still require each user to provide their own factors for authentication. |
| Device unlock factors A | First unlock factor credential providers. |
| Device unlock factors B | Second unlock factor credential providers. |
| Device unlock rules | Signal rules for device unlock. |
| Dynamic lock factors | If you enable this setting, these signal rules will be evaluated to detect user absence and automatically lock the device. |
| Dynamic lock rules | Signal rules for the dynamic lock. |
| Turn off smart card emulation | If you enable this setting, Windows Hello for Business provisions Windows Hello for Business credentials that are not compatible with smart card applications. |
| Use a hardware security device | If you enable this setting, Windows Hello for Business provisioning only occurs on devices with usable 1.2 or 2.0 TPMs. You can optionally exclude security devices, which prevents Windows Hello for Business provisioning from using those devices. |
| Do not use the tpm1.2 security devices | Exclude TPM 1.2 security devices. |
| Use biometrics | If you enable or do not configure this setting, Windows Hello for Business allows the use of biometric gestures. |
| Use certificate for on-premises authentication | If you enable this setting, Windows Hello for Business enrolls a sign-in certificate that is used for on-premises authentication. |
| Use PIN Recovery | If you enable this setting, Windows Hello for Business uses the PIN recovery service. |
| Use Windows Hello for Business certificates as smart card certificates | If you enable this setting, applications use Windows Hello for Business certificates as smart card certificates. Biometric factors are unavailable when a user is asked to authorize the use of the certificate's private key. |
| Use Windows Hello for Business | If you enable this setting, the device provisions Windows Hello for Business using keys or certificates for all users. |
| Do not start Windows Hello provisioning after sign-in | If you enable this setting, Windows Hello for Business does not automatically start provisioning after the user has signed in. |
The setting of the TPM group:
| Name | Description |
| The level of TPM owner authorization information available to the operating system | This policy setting configures how much of the TPM owner authorization information is stored in the registry of the local computer. Depending on the amount of TPM owner authorization information stored locally, the operating system and TPM-based applications can perform certain TPM actions that require TPM owner authorization without requiring the user to enter the TPM owner password. You can choose to have the operating system store either the full TPM owner authorization value, the TPM administrative delegation blob plus the TPM user delegation blob, or none. If you enable this policy setting, Windows will store the TPM owner authorization in the registry of the local computer according to the operating system managed TPM authentication setting you chose. |
| Configure the system to clear the TPM if it is not in a ready state | This policy setting configures the system to prompt the user to clear the TPM if the TPM is detected to be in any state other than Ready. This policy will take effect only if the system's TPM is in a state other than Ready, including if the TPM is "Ready, with reduced functionality". The prompt to clear the TPM will start occurring after the next reboot, upon user login only if the logged-in user is part of the Administrators group for the system. The prompt can be dismissed but will reappear after every reboot and login until the policy is disabled or until the TPM is in a Ready state. |
| Configure the system to use legacy Dictionary Attack Prevention Parameters setting for TPM 2.0 | This policy setting configures the TPM to use the Dictionary Attack Prevention Parameters (lockout threshold and recovery time) to the values that were used for Windows 10 Version 1607 and below. Setting this policy will take effect only if a) the TPM was originally prepared using a version of Windows after Windows 10 Version 1607 and b) the System has a TPM 2.0. Note that enabling this policy will only take effect after the TPM maintenance task runs (which typically happens after a system restart). Once this policy has been enabled on a system and has taken effect (after a system restart), disabling it will have no impact, and the system's TPM will remain configured using the legacy Dictionary Attack Prevention parameters, regardless of the value of this group policy. The only way for the disabled setting of this policy to take effect on a system where it was once enabled is to a) disable it from group policy and b)clear the TPM on the system. |
| Ignore the default list of blocked TPM commands | If you enable this policy setting, Windows will ignore the computer's default list of blocked TPM commands and will only block those TPM commands specified by Group Policy or the local list. |
| Ignore the local list of blocked TPM commands | If you enable this policy setting, Windows will ignore the computer's local list of blocked TPM commands and will only block those TPM commands specified by Group Policy or the default list. |
| Standard User Individual Lockout Threshold | This policy setting allows you to manage the maximum number of authorization failures for each standard user for the Trusted Platform Module (TPM). If the number of authorization failures for the user within the duration for Standard User Lockout Duration equals this value, the standard user is prevented from sending commands to the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that require authorization. This setting helps administrators prevent the TPM hardware from entering a lockout mode because it slows the speed standard users can send commands requiring authorization to the TPM. If this value is not configured, a default value of 4 is used. |
| Standard User Lockout Duration | This policy setting allows you to manage the duration in minutes for counting standard user authorization failures for Trusted Platform Module (TPM) commands requiring authorization. If the number of TPM commands with an authorization failure within the duration equals a threshold, a standard user is prevented from sending commands requiring authorization to the TPM. If this value is not configured, a default value of 480 minutes (8 hours) is used. |
| Standard User Total Lockout Threshold | This policy setting allows you to manage the maximum number of authorization failures for all standard users for the Trusted Platform Module (TPM). If the total number of authorization failures for all standard users within the duration for Standard User Lockout Duration equals this value, all standard users are prevented from sending commands to the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that require authorization. This setting helps administrators prevent the TPM hardware from entering a lockout mode because it slows the speed standard users can send commands requiring authorization to the TPM. If this value is not configured, a default value of 9 is used. |
| Turn on TPM backup to Active Directory Domain Services (1 of 2) | If you enable these 2 settings, TPM owner information will be automatically and silently backed up to AD DS when you use Windows to set or change a TPM owner password. |
| Turn on TPM backup to Active Directory Domain Services (2 of 2) | If you enable these 2 settings, TPM owner information will be automatically and silently backed up to AD DS when you use Windows to set or change a TPM owner password. |
The setting of the Local security group:
| Name | Description |
| Accounts: Limit local account use of blank passwords to console logon only | This security setting determines whether local accounts that are not password protected can be used to log on from locations other than the physical computer console. If enabled, local accounts that are not password protected will only be able to log on at the computer's keyboard. |
| Audit: Audit the access of global system objects | This security setting determines whether to audit the access of global system objects. If this policy is enabled, it causes system objects, such as mutexes, events, semaphores and DOS devices, to be created with a default system access control list (SACL). Only named objects are given a SACL; SACLs are not given to objects without names. If the Audit object access audit policy is also enabled, access to these system objects is audited. |
| Audit: Audit the use of Backup and Restore privilege | This security setting determines whether to audit the use of all user privileges, including Backup and Restore, when the Audit privilege use policy is in effect. Enabling this option when the Audit privilege use policy is also enabled generates an audit event for every file that is backed up or restored.0 - Disabled, 1 - Enabled |
| Audit: Force audit policy subcategory settings to override audit policy category settings | Windows Vista and later versions of Windows allow audit policy to be managed in a more precise way using audit policy subcategories. Setting audit policy at the category level will override the new subcategory audit policy feature. Group Policy only allows audit policy to be set at the category level, and existing group policy may override the subcategory settings of new machines as they are joined to the domain or upgraded to Windows Vista or later versions. To allow audit policy to be managed using subcategories without requiring a change to Group Policy, there is a new registry value in Windows Vista and later versions, SCENoApplyLegacyAuditPolicy, which prevents the application of category-level audit policy from Group Policy and from the Local Security Policy administrative tool. |
| Audit: Shut down system immediately if unable to log security audits | This security setting determines whether the system shuts down if it is unable to log security events. If this security setting is enabled, it causes the system to stop if a security audit cannot be logged for any reason. Typically, an event fails to be logged when the security audit log is full and the retention method that is specified for the security log is either Do Not Overwrite Events or Overwrite Events by Days. |
| DCOM: Machine Access Restrictions in Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL) syntax | This policy setting determines which users or groups can access DCOM application remotely or locally. This setting is used to control the attack surface of the computer for DCOM applications. |
| DCOM: Machine Launch Restrictions in Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL) syntax | This policy setting determines which users or groups can launch or activate DCOM applications remotely or locally. This setting is used to control the attack surface of the computer for DCOM applications |
| Devices: Allow undock without having to log on | This security setting determines whether a portable computer can be undocked without having to log on. If this policy is enabled, logon is not required and an external hardware eject button can be used to undock the computer. If disabled, a user must log on and have the Remove computer from docking station privilege to undock the computer. |
| Devices: Allowed to format and eject removable media | This security setting determines who is allowed to format and eject removable NTFS media. 0 - Only administrators of the computer, 1 - Only administrators and power users, 2 - Only administrators and the local current user. |
| Devices: Prevent users from installing printer drivers | For a computer to print to a shared printer, the driver for that shared printer must be installed on the local computer. This security setting determines who is allowed to install a printer driver as part of connecting to a shared printer. If this setting is enabled, only Administrators can install a printer driver as part of connecting to a shared printer. If this setting is disabled, any user can install a printer driver as part of connecting to a shared printer. |
| Devices: Restrict CD-ROM access to locally logged-on user only | This security setting determines whether a CD-ROM is accessible to both local and remote users simultaneously. If this policy is enabled, it allows only the interactively logged-on user to access removable CD-ROM media. If this policy is enabled and no one is logged on interactively, the CD-ROM can be accessed over the network. 1- Enabled, 2 - Disabled. |
| Devices: Restrict floppy access to locally logged-on user only | This security setting determines whether removable floppy media are accessible to both local and remote users simultaneously. If this policy is enabled, it allows only the interactively logged-on user to access removable floppy media. 1- Enabled, 2 - Disabled. |
| Devices: Unsigned driver installation behavior | This security setting determines what happens when an attempt is made to install a device driver (by means of Setup API) that has not been tested by the Windows Hardware Quality Lab (WHQL).The options are: 0 - Silently succeed, 1- Warn but allow installation, 2 - Do not allow installation |
| Domain controller: Allow server operators to schedule tasks | This security setting determines if Server Operators are allowed to submit jobs by means of the AT schedule facility. |
| Domain controller: LDAP server signing requirements | This security setting determines whether the LDAP server requires signing to be negotiated with LDAP clients. |
| Domain controller: Refuse machine account password changes | This security setting determines whether domain controllers will refuse requests from member computers to change computer account passwords. By default, member computers change their computer account passwords every 30 days. If enabled, the domain controller will refuse computer account password change requests. |
| Domain member: Digitally encrypt or sign secure channel data (always) | This security setting determines whether all secure channel traffic initiated by the domain member must be signed or encrypted. |
| Domain member: Digitally encrypt secure channel data (when possible) | This security setting determines whether a domain member attempts to negotiate encryption for all secure channel traffic that it initiates. |
| Domain member: Digitally sign secure channel data (when possible) | This security setting determines whether a domain member attempts to negotiate signing for all secure channel traffic that it initiates. |
| Domain member: Disable machine account password changes | Determines whether a domain member periodically changes its computer account password. If this setting is enabled, the domain member does not attempt to change its computer account password. If this setting is disabled, the domain member attempts to change its computer account password as specified by the setting for Domain Member: Maximum age for machine account password, which by default is every 30 days. |
| Domain member: Require strong (Windows 2000 or later) session key | This security setting determines whether 128-bit key strength is required for encrypted secure channel data. |
| Interactive logon: Do not display last user name | This security setting determines whether the name of the last user to log on to the computer is displayed in the Windows logon screen. If this policy is enabled, the name of the last user to successfully log on is not displayed in the Logon Screen. |
| Interactive Logon: Display user information when session is locked | Interactive Logon: Display user information when session is locked. |
| Interactive logon: Do not require CTRL+ALT+DEL | This security setting determines whether pressing CTRL+ALT+DEL is required before a user can log on. |
| Interactive logon: Message text for users attempting to logon | This security setting specifies a text message that is displayed to users when they log on. This text is often used for legal reasons, for example, to warn users about the ramifications of misusing company information or to warn them that their actions may be audited. |
| Interactive logon: Message title for users attempting to logon | This security setting allows the specification of a title to appear in the title bar of the window that contains the Interactive logon: Message text for users attempting to log on. |
| Interactive logon: Number of previous logons to cache (in case domain controller is not available) | All previous users' logon information is cached locally so that, in the event that a domain controller is unavailable during subsequent logon attempts, they are able to log on. In this policy setting, a value of 0 disables logon caching. Any value above 50 only caches 50 logon attempts. |
| Interactive logon: Prompt user to change password before expiration | Determines how far in advance (in days) users are warned that their password is about to expire. With this advance warning, the user has time to construct a password that is sufficiently strong. |
| Interactive logon: Require Domain Controller authentication to unlock workstation | Logon information must be provided to unlock a locked computer. For domain accounts, this security setting determines whether a domain controller must be contacted to unlock a computer. If this setting is disabled, a user can unlock the computer using cached credentials. If this setting is enabled, a domain controller must authenticate the domain account that is being used to unlock the computer. |
| Interactive logon: Require smart card | This security setting requires users to log on to a computer using a smart card. |
| Interactive logon: Smart card removal behavior | This security setting determines what happens when the smart card for a logged-on user is removed from the smart card reader. 0 - No Action, 1 - Lock workstation, 2 - Force logoff, 3 - Disconnect if a remote Remote Desktop Services session. |
| Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (always) | This security setting determines whether packet signing is required by the SMB client component. The server message block (SMB) protocol provides the basis for Microsoft file and print sharing and many other networking operations, such as remote Windows administration. To prevent man-in-the-middle attacks that modify SMB packets in transit, the SMB protocol supports the digital signing of SMB packets. This policy setting determines whether SMB packet signing must be negotiated before further communication with an SMB server is permitted. |
| Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (if server agrees) | This security setting determines whether the SMB client attempts to negotiate SMB packet signing. The server message block (SMB) protocol provides the basis for Microsoft file and print sharing and many other networking operations, such as remote Windows administration. To prevent man-in-the-middle attacks that modify SMB packets in transit, the SMB protocol supports the digital signing of SMB packets. This policy setting determines whether the SMB client component attempts to negotiate SMB packet signing when it connects to an SMB server. |
| Microsoft network client: Send unencrypted password to third-party SMB servers | If this security setting is enabled, the Server Message Block (SMB) redirector is allowed to send plaintext passwords to non-Microsoft SMB servers that do not support password encryption during authentication. |
| Microsoft network server: Amount of idle time required before suspending session | This security setting determines the amount of continuous idle time (in minutes) that must pass in a Server Message Block (SMB) session before the session is suspended due to inactivity. Administrators can use this policy to control when a computer suspends an inactive SMB session. If client activity resumes, the session is automatically reestablished. |
| Microsoft network server: Digitally sign communications (always) | This security setting determines whether packet signing is required by the SMB server component. The server message block (SMB) protocol provides the basis for Microsoft file and print sharing and many other networking operations, such as remote Windows administration. To prevent "man-in-the-middle" attacks that modify SMB packets in transit, the SMB protocol supports the digital signing of SMB packets. This policy setting determines whether SMB packet signing must be negotiated before further communication with an SMB client is permitted. |
| Microsoft network server: Digitally sign communications (if client agrees) | This security setting determines whether the SMB server will negotiate SMB packet signing with clients that request it. The server message block (SMB) protocol provides the basis for Microsoft file and print sharing and many other networking operations, such as remote Windows administration. To prevent man-in-the-middle attacks that modify SMB packets in transit, the SMB protocol supports the digital signing of SMB packets. This policy setting determines whether the SMB server will negotiate SMB packet signing when an SMB client requests it. |
| Microsoft network server: Disconnect clients when logon hours expire | This security setting determines whether to disconnect users who are connected to the local computer outside their user account's valid logon hours. This setting affects the Server Message Block (SMB) component. |
| Microsoft network server: Server SPN target name validation level | The server message block (SMB) protocol provides the basis for file and printer sharing and many other networking operations, such as remote Windows administration. The SMB protocol supports validating the SMB server service principal name (SPN) within the authentication blob provided by a SMB client to prevent a class of attacks against SMB servers referred to as SMB relay attacks. This setting will affect both SMB1 and SMB2. |
| Network access: Do not allow anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts | This security setting determines what additional permissions will be granted for anonymous connections to the computer. Windows allows anonymous users to perform certain activities, such as enumerating the names of domain accounts and network shares. This is convenient, for example, when an administrator wants to grant access to users in a trusted domain that does not maintain a reciprocal trust. |
| Network access: Do not allow anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts and shares | This security setting determines whether anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts and shares is allowed. Windows allows anonymous users to perform certain activities, such as enumerating the names of domain accounts and network shares. This is convenient, for example, when an administrator wants to grant access to users in a trusted domain that does not maintain a reciprocal trust. |
| Network access: Do not allow storage of passwords and credentials for network authentication | This security setting determines whether Stored User Names and Passwords saves passwords, credentials, or .NET Passports for later use when it gains domain authentication. If it is enabled, this setting prevents the Stored User Names and Passwords from storing passwords and credentials. |
| Network access: Let Everyone permissions apply to anonymous users | This security setting determines what additional permissions are granted for anonymous connections to the computer. |
| Network access: Named Pipes that can be accessed anonymously | This security setting determines which communication sessions (pipes) will have attributes and permissions that allow anonymous access. |
| Network access: Remotely accessible registry paths | This security setting determines which registry keys can be accessed over the network, regardless of the users or groups listed in the access control list (ACL) of the winreg registry key. |
| Network access: Remotely accessible registry paths and sub-paths | This security setting determines which registry paths and subpaths can be accessed over the network, regardless of the users or groups listed in the access control list (ACL) of the winreg registry key. |
| Network access: Shares that can be accessed anonymously | This security setting determines which network shares can accessed by anonymous users. |
| Network access: Sharing and security model for local accounts | This security setting determines how network logons that use local accounts are authenticated. If this setting is set to Classic, network logons that use local account credentials authenticate by using those credentials. The Classic model allows fine control over access to resources. By using the Classic model, you can grant different types of access to different users for the same resource. |
| Network security: Do not store LAN Manager hash value on next password change | This security setting determines if, at the next password change, the LAN Manager (LM) hash value for the new password is stored. The LM hash is relatively weak and prone to attack, as compared with the cryptographically stronger Windows NT hash. Since the LM hash is stored on the local computer in the security database the passwords can be compromised if the security database is attacked. |
| Network security: LAN Manager authentication level | This security setting determines which challenge/response authentication protocol is used for network logons. |
| Network security: LDAP client signing requirements | This security setting determines the level of data signing that is requested on behalf of clients issuing LDAP BIND requests. |
| Network security: Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based (including secure RPC) clients | This security setting allows a client to require the negotiation of 128-bit encryption and/or NTLMv2 session security. These values are dependent on the LAN Manager Authentication Level security setting value. |
| Network security: Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based (including secure RPC) servers | This security setting allows a server to require the negotiation of 128-bit encryption and/or NTLMv2 session security. These values are dependent on the LAN Manager Authentication Level security setting value. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers | This policy setting allows you to deny or audit outgoing NTLM traffic from this Windows 7 or this Windows Server 2008 R2 computer to any Windows remote server. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic | This policy setting allows you to deny or allow incoming NTLM traffic. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Audit Incoming NTLM Traffic | This policy setting allows you to audit incoming NTLM traffic. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: NTLM authentication in this domain | This policy setting allows you to deny or allow NTLM authentication within a domain from this domain controller. This policy does not affect interactive logon to this domain controller. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Audit NTLM authentication in this domain | This policy setting allows you to audit NTLM authentication in a domain from this domain controller. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Add remote server exceptions for NTLM authentication | This policy setting allows you to create an exception list of remote servers to which clients are allowed to use NTLM authentication if the "Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers" policy setting is configured. |
| Network security: Restrict NTLM: Add server exceptions in this domain | This policy setting allows you to create an exception list of servers in this domain to which clients are allowed to use NTLM pass-through authentication if the "Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Deny NTLM authentication in this domain" is set. |
| Network security: Allow LocalSystem NULL session fallback | Allow NTLM to fall back to NULL session when used with LocalSystem. |
| Network security: Allow PKU2U authentication requests to this computer to use online identities | This policy will be turned off by default on domain joined machines. This would disallow the online identities to be able to authenticate to the domain joined machine in Windows 7. |
| Network security: Configure encryption types allowed for Kerberos | This policy setting allows you to set the encryption types that Kerberos is allowed to use. If not selected, the encryption type will not be allowed. This setting may affect compatibility with client computers or services and applications. |
| Recovery console: Allow automatic administrative logon | This security setting determines if the password for the Administrator account must be given before access to the system is granted. If this option is enabled, the Recovery Console does not require you to provide a password, and it automatically logs on to the system. |
| Recovery console: Allow floppy copy and access to all drives and all folders | Enabling this security option makes the Recovery Console SET command available, which allows you to set the following Recovery Console environment variables. |
| Shutdown: Allow system to be shut down without having to log on | This security setting determines whether a computer can be shut down without having to log on to Windows. When this policy is enabled, the Shut Down command is available on the Windows logon screen. |
| Shutdown: Clear virtual memory pagefile | This security setting determines whether the virtual memory pagefile is cleared when the system is shut down. |
| System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing | For the Schannel Security Service Provider (SSP), this security setting disables the weaker Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols and supports only the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols as a client and as a server (if applicable). If this setting is enabled, Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer (TLS/SSL) Security Provider uses only the FIPS 140 approved cryptographic algorithms: 3DES and AES for encryption, RSA or ECC public key cryptography for the TLS key exchange and authentication, and only the Secure Hashing Algorithm (SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, and SHA512) for the TLS hashing requirements. |
| System cryptography: Force strong key protection for user keys stored on the computer | This security setting determines if users' private keys require a password to be used. |
| System objects: Default owner for objects created by members of the Administrators group | This security setting determines which security principal (SID) will be assigned the OWNER of objects when the object is created by a member of the Administrators Group. |
| System objects: Require case insensitivity for non-Windows subsystems | This security setting determines whether case insensitivity is enforced for all subsystems. The Win32 subsystem is case insensitive. However, the kernel supports case sensitivity for other subsystems, such as POSIX. |
| System objects: Strengthen default permissions of internal system objects (e.g., Symbolic Links) | This security setting determines the strength of the default discretionary access control list (DACL) for objects. |
| System settings: Optional subsystems | This security setting determines which subsystems can optionally be started up to support your applications. With this security setting, you can specify as many subsystems to support your applications as your environment demands. |
| System settings: Use Certificate Rules on Windows Executables for Software Restriction Policies | This security setting determines if digital certificates are processed when a user or process attempts to run software with an .exe file name extension. This security settings is used to enable or disable certificate rules, a type of software restriction policies rule. With software restriction policies, you can create a certificate rule that will allow or disallow software that is signed by Authenticode to run, based on the digital certificate that is associated with the software. In order for certificate rules to take effect, you must enable this security setting. |
| User Account Control: Admin Approval Mode for the Built-in Administrator account | This security setting determines the behavior of Admin Approval mode for the Built-in Administrator account. |
| User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators in Admin Approval Mode | This security setting determines the behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators. |
| User Account Control: Behavior of the elevation prompt for standard users | This security setting determines the behavior of the elevation prompt for standard users. |
| User Account Control: Detect application installations and prompt for elevation | This security setting determines the behavior of application installation detection for the entire system. |
| User Account Control: Only elevate executables that are signed and validated | This security setting will enforce PKI signature checks on any interactive application that requests elevation of privilege. Enterprise administrators can control the admin application allowed list thru the population of certificates in the local computers Trusted Publisher Store. |
| User Account Control: Only elevate UIAccess applications that are installed in secure locations | This security setting will enforce the requirement that applications that request execution with a UIAccess integrity level (via a marking of UIAccess=true in their application manifest), must reside in a secure location on the file system. |
| User Account Control: Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode | This security setting determines the behavior of all UAC policies for the entire system. |
| User Account Control: Switch to the secure desktop when prompting for elevation | This security setting determines whether the elevation request will prompt on the interactive users desktop or the Secure Desktop. |
| User Account Control: Virtualize file and registry write failures to per-user locations | This security setting enables the redirection of legacy application write failures to defined locations in both the registry and file system. This feature mitigates those applications that historically ran as administrator and wrote runtime application data back to either %ProgramFiles%, %Windir%; %Windir%\system32 or HKLM\Software\.... |
| User Account Control: Allow UIAccess applications to prompt for elevation without using the secure desktop | This security setting controls whether User Interface Accessibility (UIAccess or UIA) programs can automatically disable the secure desktop for elevation prompts being used by a standard user. If you enable this setting, UIA programs including Windows Remote Assistance can automatically disable the secure desktop for elevation prompts. Unless you have also disabled elevation prompts, the prompts will appear on the interactive user's desktop instead of the secure desktop. |
Note that some options may be shown as inactive. It depends on the version of the selected Operating System.